Hair transplantation has experienced a great revolution with scientists specialized in this field. In order to achieve a good cosmetic result with hair transplantation, it is necessary to create a sufficiently dense natural hairline. With the methods described, permanent solution to hair loss has been found.
Since the concept of 'donor dominance' in male pattern baldness was first published in 1959, it remains unclear why occipital hairs are resistant to shedding. The most accepted reason is that the occipital scalp is not dependent on androgens. Regardless of the reason, hair transplantation for hair loss in both women and men is characterized by the use of permanent and resistant hair on the nape.
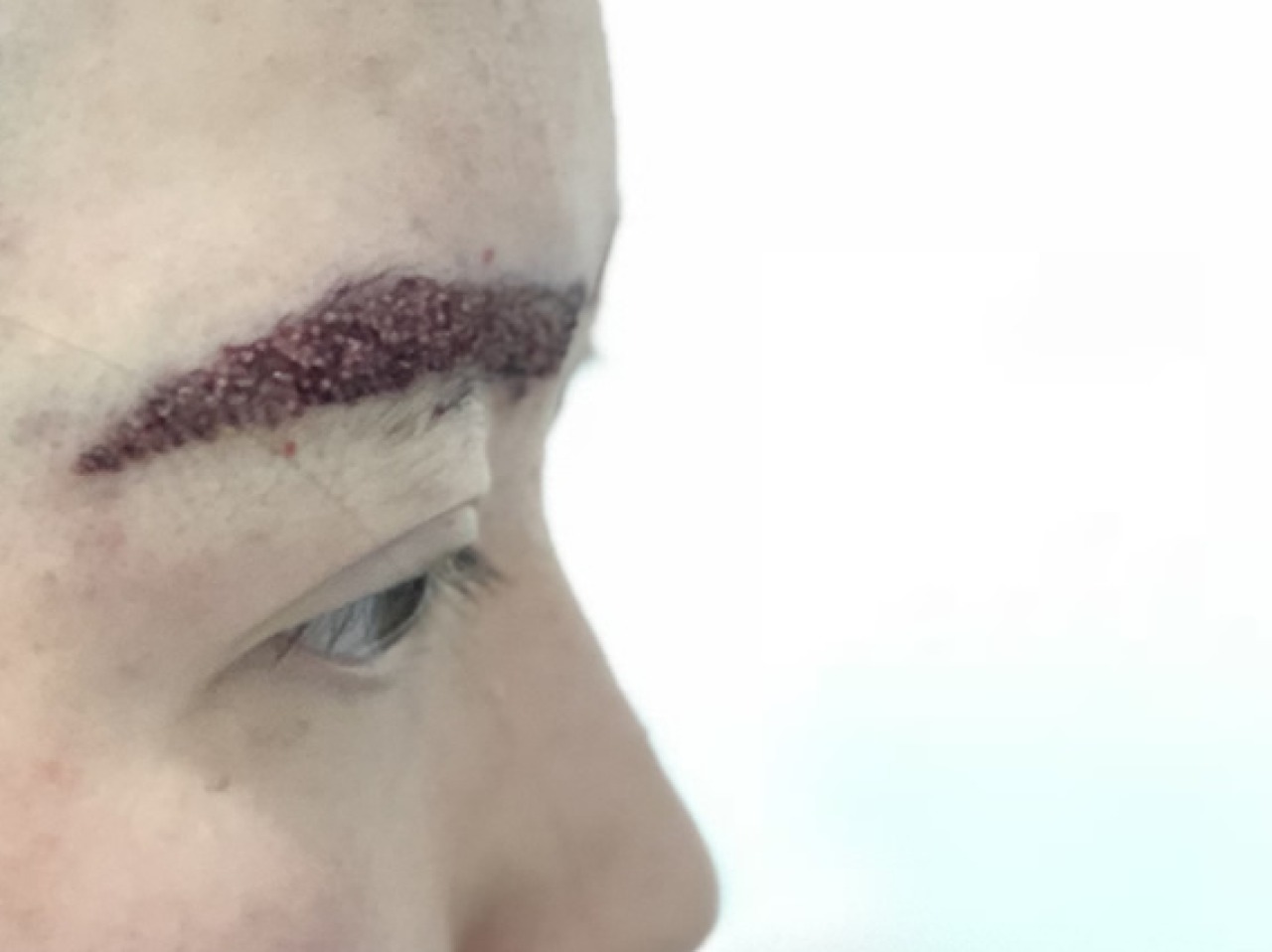
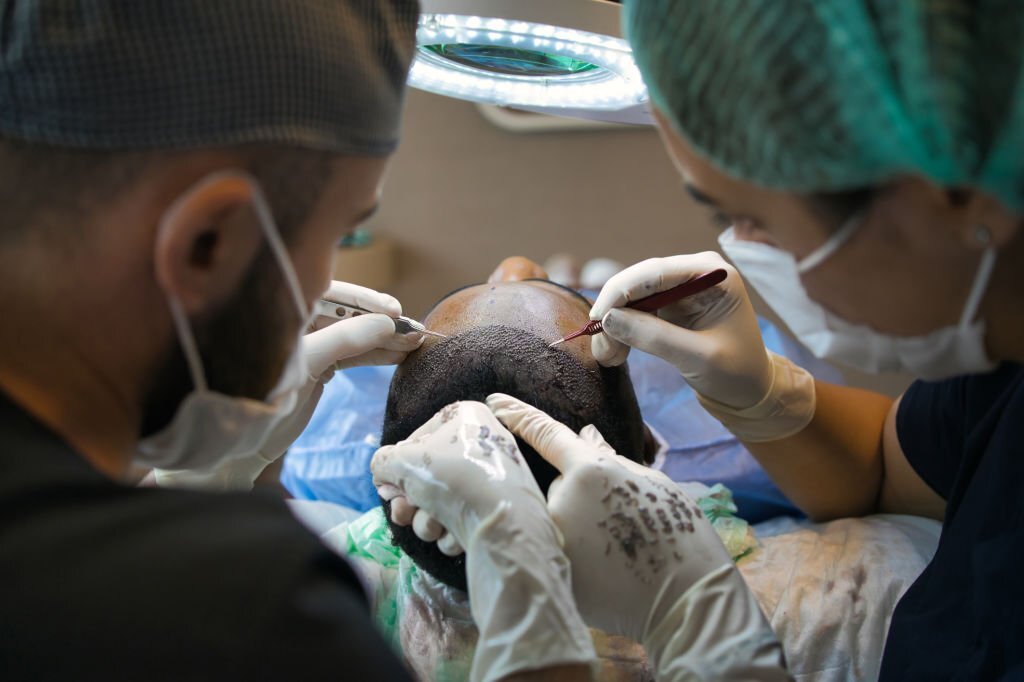
A widely used hair transplantation technique is called follicular unit transplantation (FUT). . This technique involves shaving the donor area and making an elliptical incision to collect the hair follicles. The dimensions of the ellipse are calculated until the recipient receives the graft. The donor site is carefully closed to minimize scarring. Under magnification, the additional tissues of the hair follicle and the surrounding epithelium are separated from the collected hair-bearing skin. Grafts with one, two, or three follicle clusters are placed in Petri dishes with chilled saline. The grafts are then properly placed in the recipient area. Unlike FUT, FUE is a method that uses circular thick-tipped needles to remove one or two rooted follicular units from the donor area. In addition, when compared to the FUT technique, FUE can give superior results and more follicles can be transplanted. While scars remain after FUT technique, FUE offers a scarless alternative. While FUE has some advantages over FUT, it also has some disadvantages. FUE requires more time spent on the procedure, durability, and hair short enough to be neatly gathered.
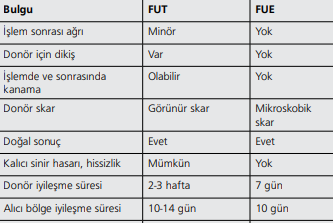
Differences between FUT and FUE technique

Differences between DHI and FUE technique
 Türkçe
Türkçe